Features for General Content Screens on the Web
The web platform includes extra features for General Content Screens that you won’t find on other platforms:
web-general-content
Screen Feed
You can add a screen feed to a web General Content Screen. This feed is optional, but if you add one, the screen will use the first item in the feed to add extra details. These details will automatically fill in the screen’s HTML title, description, and image. The screen feed also helps provide data to components within the screen. For example, if a component needs a dynamic value from an extension to set up its feed, it will pull that value from the screen feed.
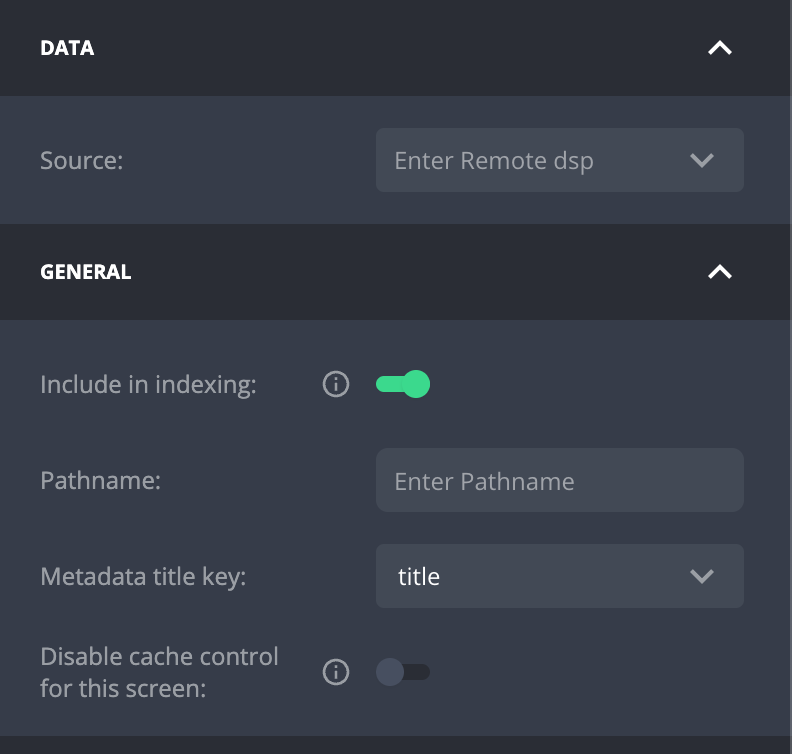
To set the screen, feed set a feed in the
DataSourcefield as shown above.
Include in indexing
All screens of the site are set to be indexed by default by Search engines (like Google). You can explicitly un-index a specific screen by unchecking the
then Include in indexing checkbox.
Screen Path (Pathname)
You can set a path for a General Content Screen by filling in the "screen path" field. The path has to start with a /. For example, if you’re creating an "About" page that users can visit at /about, you would set the path to /about.
For dynamic screens, like a "Show" page, the screen path can include variables to make each page unique.
For example, you can set the path to /shows/{{id}}, where {{id}} is a placeholder for the unique identifier of each item in the screen feed. This setup allows the web app to create a unique URL for every show based on its feed entry ID. The id value is automatically populated by the web app when the page is displayed, ensuring that the URL matches the specific content being shown.
Disabling Cache Control for a Specific Screen
By default, all screens are cached for a few minutes on the CDN to enhance performance and reduce load times. However, there may be situations where you need to disable caching for a particular screen—such as when the screen contains personalized user data or other dynamic content.
If needed, you can disable caching specifically for that screen.
In most cases, caching should remain enabled to maintain optimal performance. Only disable caching if you fully understand the impact of bypassing the cache for that specific screen.